ChatScript
Normally you have to create a whole bot from scratch, but with a ChatScript you only need to create the flow by having a conversation present. This conversation acts as a template which the ChatScript needs to follow.
The ChatScript already exists and you're able to hire this bot from the Bot store.
Invocable commands
With the ChatScript bot you have the possiblity to use multiple commands. Be sure that you've enabled the bot from the Bot Store, otherwise you can't call the ChatScript bot.
Mentions
Via a mention you can invoke multiple command of the ChatScript bot. Right now we have 4 operational commands that can be used and 3 of them are still in the pipeline. Below we have examples of the commands that are possible and how they globally work.
Start
@ChatScript start TemplateID will result in starting a conversation based on a preffered template. This also works if the setup template is different from the one in the configuration form of the ChatScript bot itself.
Load
@ChatScript load works similar to the Start command before, yet it's showing an overview of all existing templates by the bot. After that you have the oppertunity to decide which template the bot should run, in the background it's techically running the @ChatScript start TemplateID command for you.
Save
@ChatScript save will show you an overview of messages from which you can save from the current conversation. When you click the given message, it will save this to a new template for you.
Flush
@ChatScript flush TemplateID will result in deleting existing cache of a conversation within the bot. Next time the bot is triggered, it will have the new set of data ready to be ran by you.
Stop & Resume
After running a template, for example by calling: @ChatScript load it will also provide a Stop button, this will make the bot stop. When it's stopped, the conversation can also be resumed. A Resume button will show after the conversation has been stopped.
Under development
- Edit
- Record
- Create
Create Template
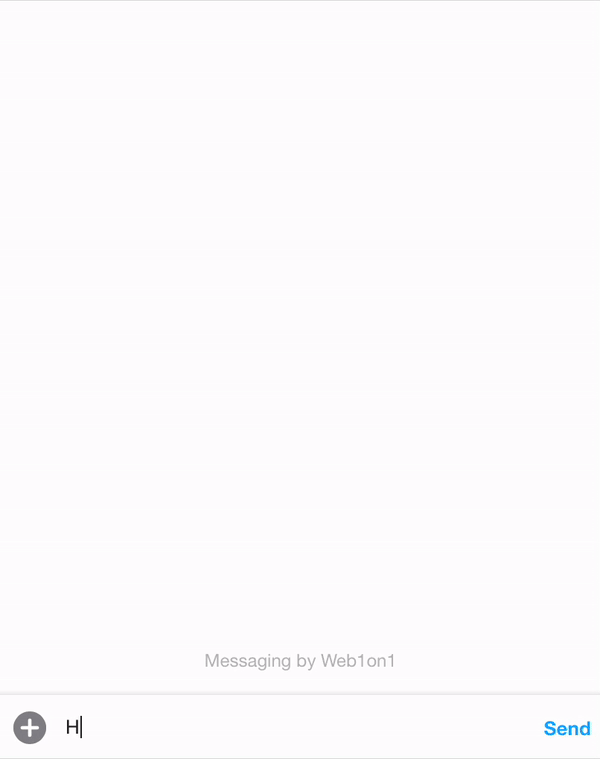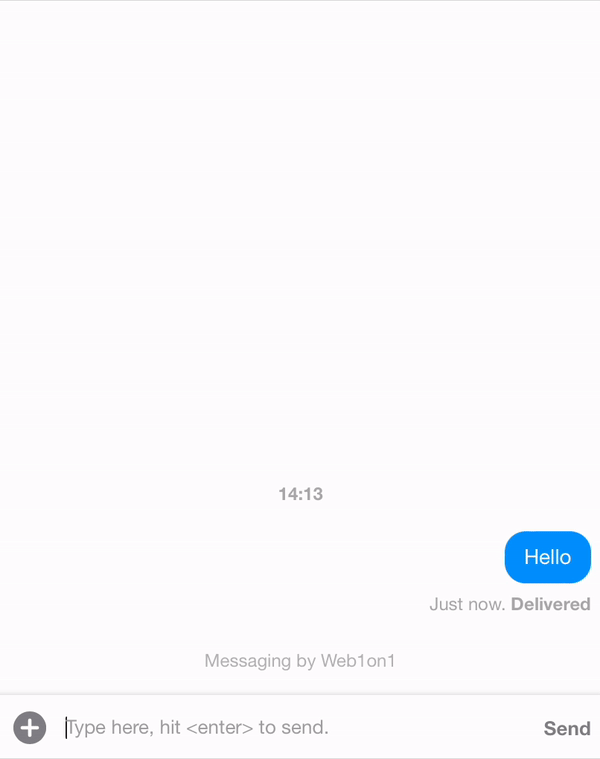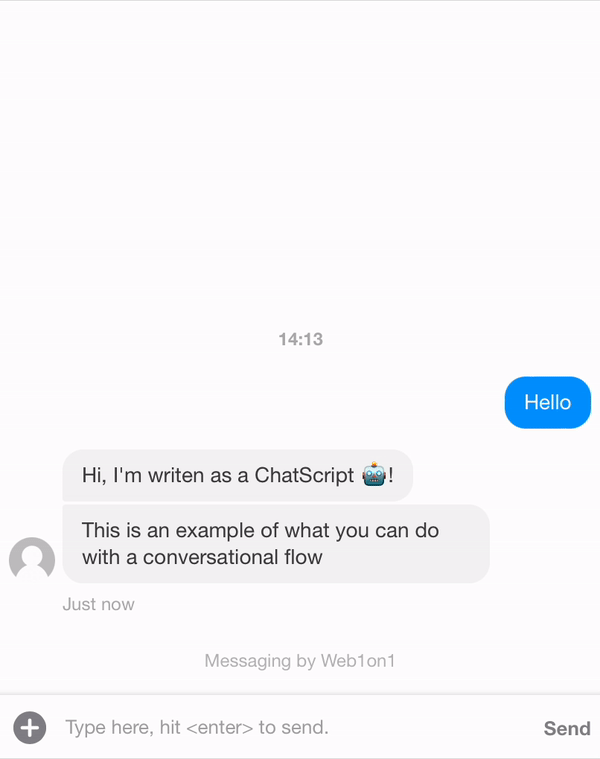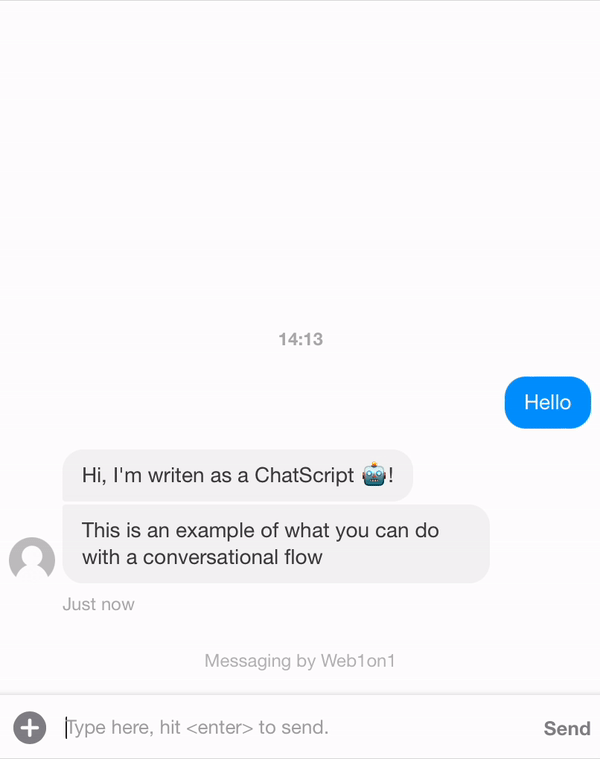
Let's create a template first. In the example below we want the ChatScript to send two messages as an agent.
The flow always starts with the first message and then follows the flow via the meta.next params that should be present at any time.
Request: POST /v2/conversations/
{ "_id": "634408fd849722965483e3c9", "organization": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "orgPath": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "type": "template", "name": "Example Conversation", "status": "closed", "messages": [ { "_id": "634408f83df375fc96bdbebd", "meta": { "next": "63440904c8780af787343178" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Hi, I'm writen as a ChatScript 🤖!" }, { "_id": "63440904c8780af787343178", "meta": { "next": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2" }, "role": "agent", "text": "This is an example of what you can do with a conversational flow" }, { "_id": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "agent", "text": "/leave", "type": "command", "delay": 5000 } ] }
Important
- Always add an underscore infront of the ID: "_id".
- Every ID needs to be unique, use a tool like MongoDB ObjectId Generator that generates an ID for you.
- Change organization and orgPath when trying to post to your own organisation.
- Last messages can be set to null
- Status of conversation is 'closed'
- Type needs to be a 'template'
- Always make the ChatScript leave at the end of the template
Update Conversation
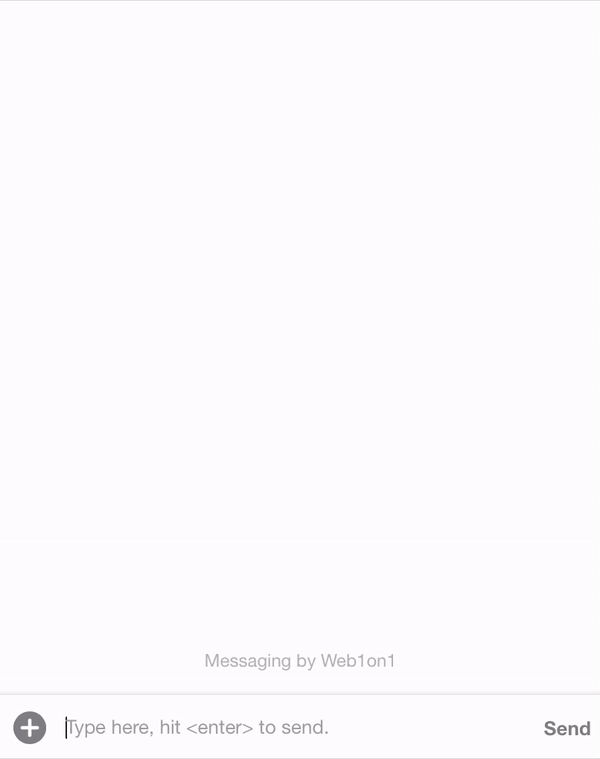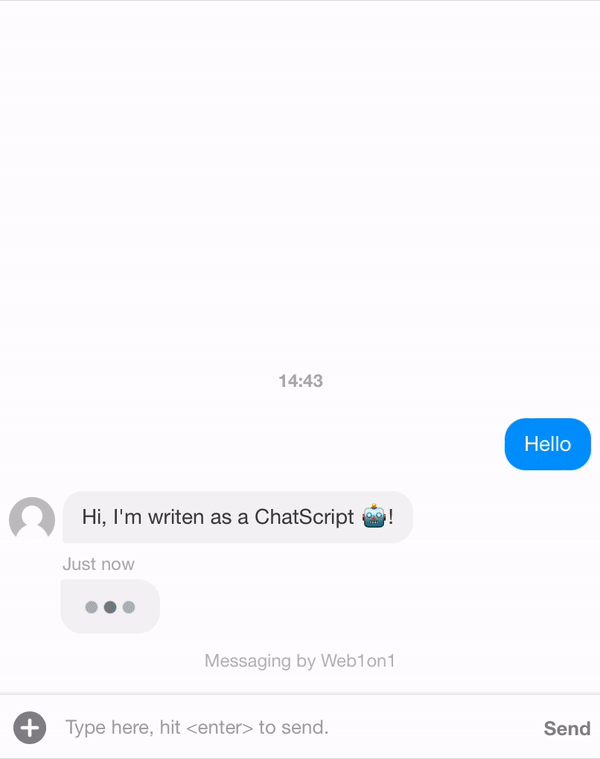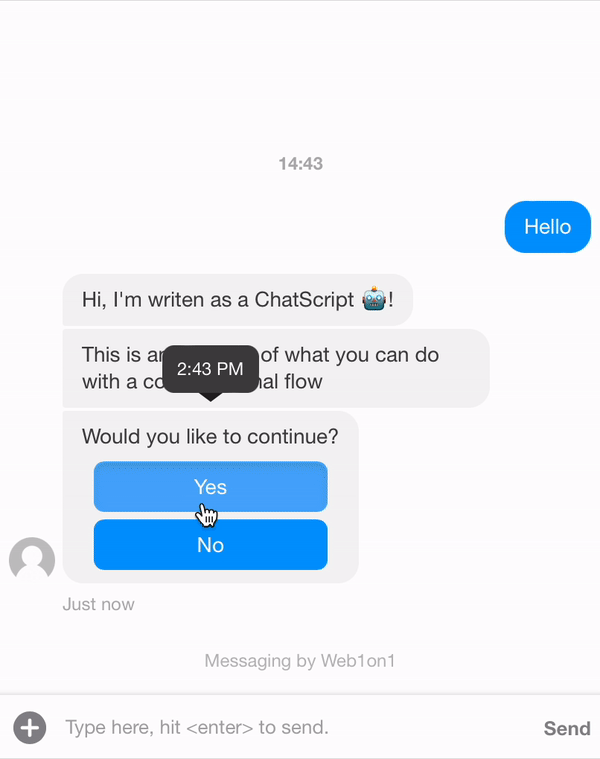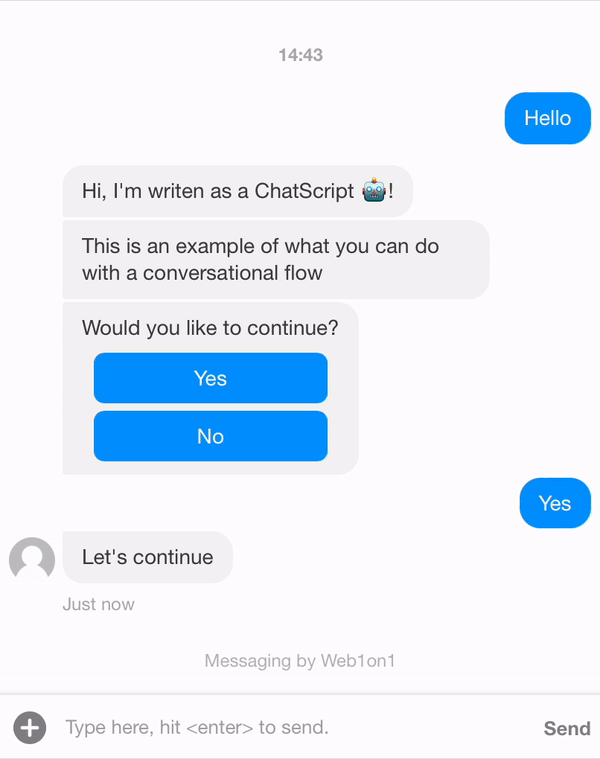
Let's say we update the conversation, add a button and contact response.
Request: DELETE /v2/conversations/634408fd849722965483e3c9
Request: POST /v2/conversations
{ "_id": "634408fd849722965483e3c9", "organization": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "orgPath": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "type": "template", "name": "Example Conversation", "status": "closed", "messages": [ { "_id": "6344127704dffa670c9a0cee", "meta": { "next": "63441289da876617b2f4a8dc" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Hi, I'm writen as a ChatScript 🤖!" }, { "_id": "63441289da876617b2f4a8dc", "meta": { "next": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a" }, "role": "agent", "text": "This is an example of what you can do with a conversational flow" }, { "_id": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a", "meta": { "next": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Would you like to continue?", "actions": [ { "type": "postback", "text": "Yes", "payload": "6344129d7bcb3e554dd26362" }, { "type": "postback", "text": "No", "payload": "634412a2bf4a1f093d3076c6" } ] }, { "_id": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "contact", "text": "Postback response..." }, { "_id": "6344129d7bcb3e554dd26362", "meta": { "next": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Let's continue" }, { "_id": "634412a2bf4a1f093d3076c6", "meta": { "next": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2" }, "role": "agent", "text": "I'll stop the conversation" }, { "_id": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "agent", "text": "/leave", "type": "command", "delay": 5000 } ] }
Important
- Update an existing conversation.
- Awaiting a contact message needs to have the role 'contact'.
- When using buttons, the contact message results in a meta.next: 'null'
- Postback payload contains the ID of the next message
Delete Conversation
Request: DELETE /v2/conversations/634408fd849722965483e3c9 Removes the conversation and
Forms, Variables & Commands
For keeping track of answers of the contact you can use a form. Create a form in your organisation and check the ID that's been given to the form (after reopening it).
Let's assume, for the example below, that we have a form with form ID: 6344255c52523a19137f37ab and name Example form. Within the form we have one field named: age.
Request: POST /v2/conversations/
{ "_id": "634408fd849722965483e3c9", "organization": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "orgPath": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "type": "template", "name": "Example Conversation", "status": "closed", "messages": [ { "_id": "6344239315dc9888dc428ade", "meta": { "next": "6344127704dffa670c9a0cee", "form": "6344255c52523a19137f37ab" }, "type": "form", "text": "+Example form" }, { "_id": "6344127704dffa670c9a0cee", "meta": { "next": "63441289da876617b2f4a8dc" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Hi, I'm writen as a ChatScript 🤖!" }, { "_id": "63441289da876617b2f4a8dc", "meta": { "next": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a" }, "role": "agent", "text": "This is an example of what you can do with a conversational flow" }, { "_id": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a", "meta": { "next": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc" }, "role": "agent", "text": "What is your age?" }, { "_id": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc", "meta": { "next": "6344129d7bcb3e554dd26362", "form": "6344255c52523a19137f37ab" }, "role": "contact", "text": "age..." }, { "_id": "6344129d7bcb3e554dd26362", "meta": { "next": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2" }, "role": "agent", "text": ".age" }, { "_id": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "agent", "text": "/leave", "type": "command", "delay": 5000 } ] }
Same as within the App, you can also use variables within a template, in the example above age is retrieved from the form. Further more you commands like /leave or /send can be used, in this case to leave the conversation or to send the form that's been filled in by the bot.
Conditions
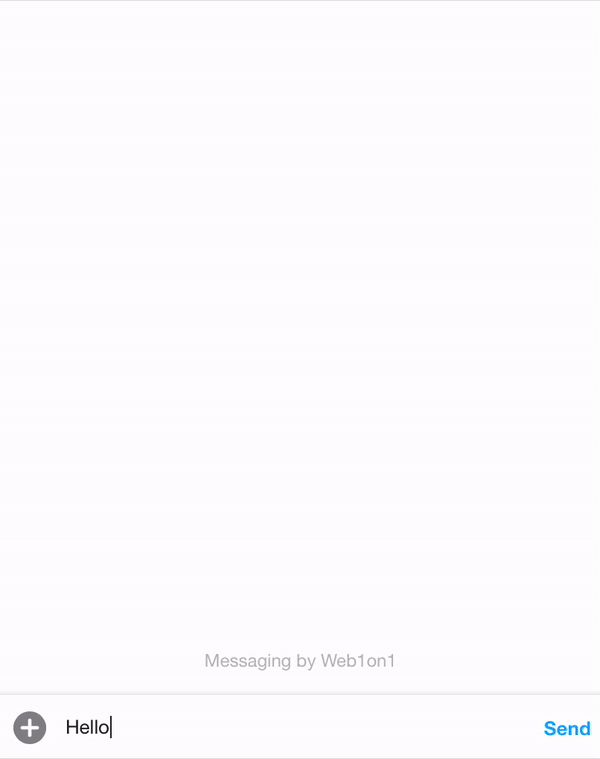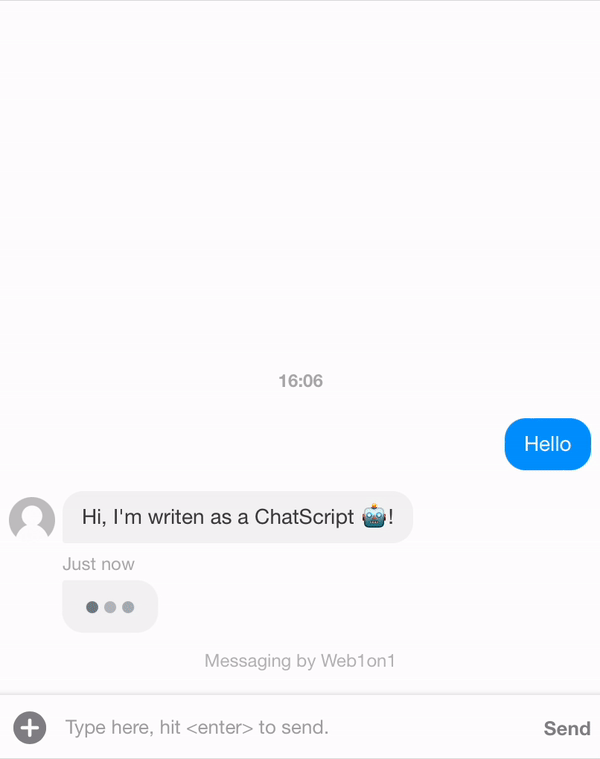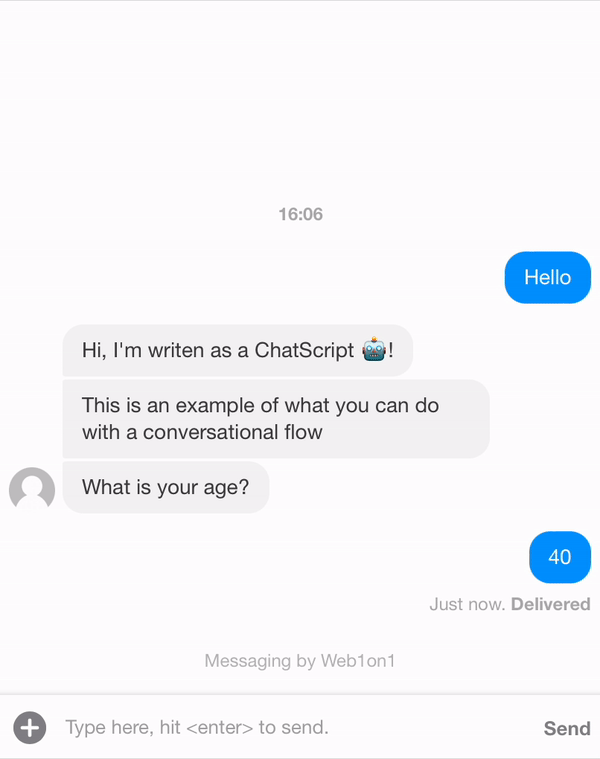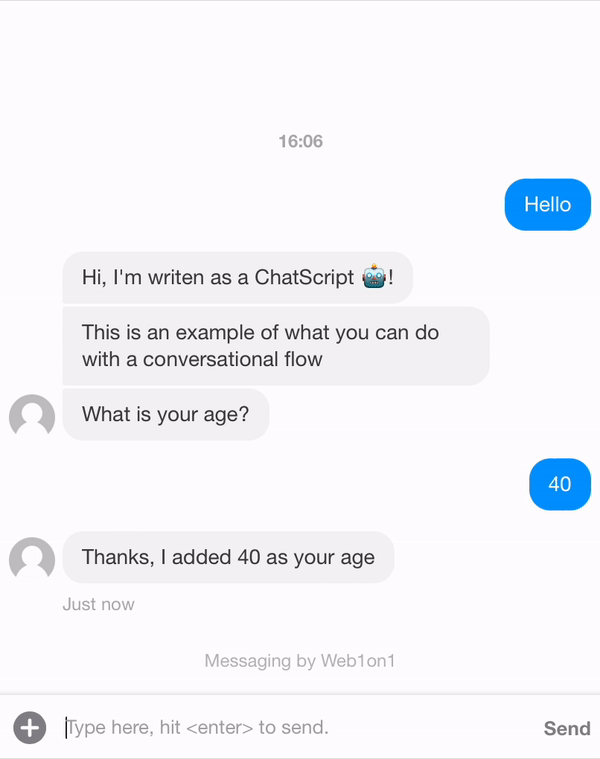
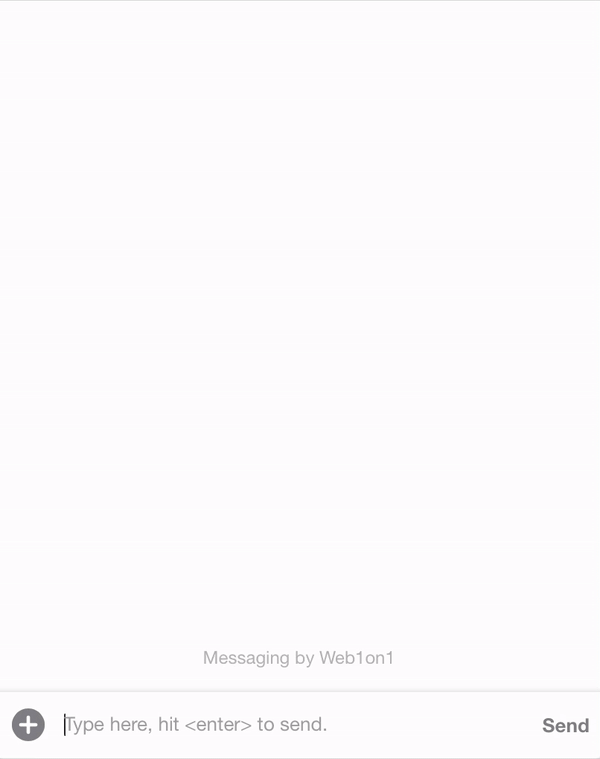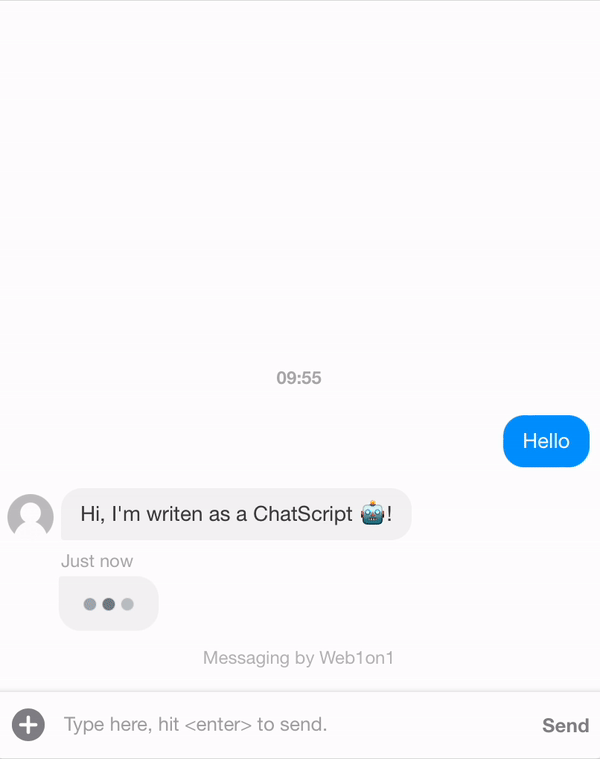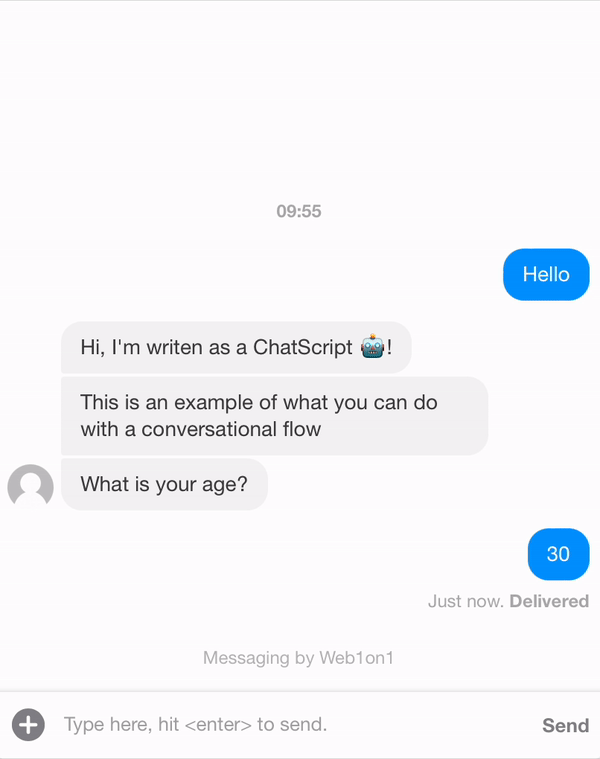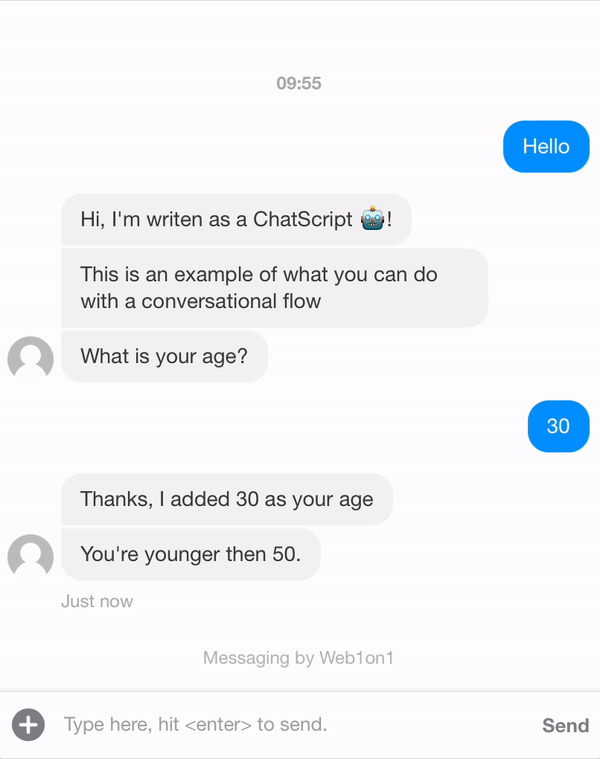
Sometimes there are multiple paths possible within a flow. Some parts can be done by buttons (as seen above), but sometimes you need to make decisions based on earlier given answer.
Below is an example of the bot telling you if you're younger or older then 50 years old, based on the age that's been given and set in the form.
Request: POST /v2/conversations/
{ "_id": "634408fd849722965483e3c9", "organization": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "orgPath": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "type": "template", "name": "Example Conversation", "status": "closed", "messages": [ { "_id": "6344239315dc9888dc428ade", "meta": { "next": "6344127704dffa670c9a0cee", "form": "6344255c52523a19137f37ab" }, "type": "form", "text": "+Example form" }, { "_id": "6344127704dffa670c9a0cee", "meta": { "next": "63441289da876617b2f4a8dc" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Hi, I'm writen as a ChatScript 🤖!" }, { "_id": "63441289da876617b2f4a8dc", "meta": { "next": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a" }, "role": "agent", "text": "This is an example of what you can do with a conversational flow" }, { "_id": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a", "meta": { "next": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc" }, "role": "agent", "text": "What is your age?" }, { "_id": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc", "meta": { "next": "6344129d7bcb3e554dd26362", "form": "6344255c52523a19137f37ab" }, "role": "contact", "text": "age..." }, { "_id": "6344129d7bcb3e554dd26362", "meta": { "next": "634425f22d907edf530660da", "form": "6344255c52523a19137f37ab" }, "type": "field", "text": ".age" }, { "_id": "634425f22d907edf530660da", "meta": { "next": null, "conditions": [ { "next": "63442b70dae72b60bcdde390", "rules": [ { "property": "form.age", "op": "lt", "value": "50" } ], "satisfy": "ALL" }, { "next": "63442b9dd836d800dca0eb6f", "rules": [ { "property": "form.age", "op": "gt", "value": "50" } ], "satisfy": "ALL" } ] }, "role": "agent", "text": "Thanks, I added {{form.Example form.age}} as your age" }, { "_id": "63442b70dae72b60bcdde390", "meta": { "next": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2" }, "role": "agent", "text": "You're younger then 50." }, { "_id": "63442b9dd836d800dca0eb6f", "meta": { "next": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2" }, "role": "agent", "text": "You're older then 50." }, { "_id": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "agent", "text": "/leave", "type": "command", "delay": 5000 } ] }
For this logic we used json-conditions, for the supported operators the npm package.
Property is the value that's been checked, in this example age, and satisfy has two options: ANY or ALL. ANY means one of the rules needs to be satisfied and when ALL is set applies to all the rules.
Supports:
- Form fields values
- Message values: text, type, isBackchannel, contentType, touchpoint, points and chatpoints
- Conversation values: touchpoint and meta variables
Modules
In the example above we use static data, but in case of having variable data you can use modules.
Request: POST /v2/conversations/
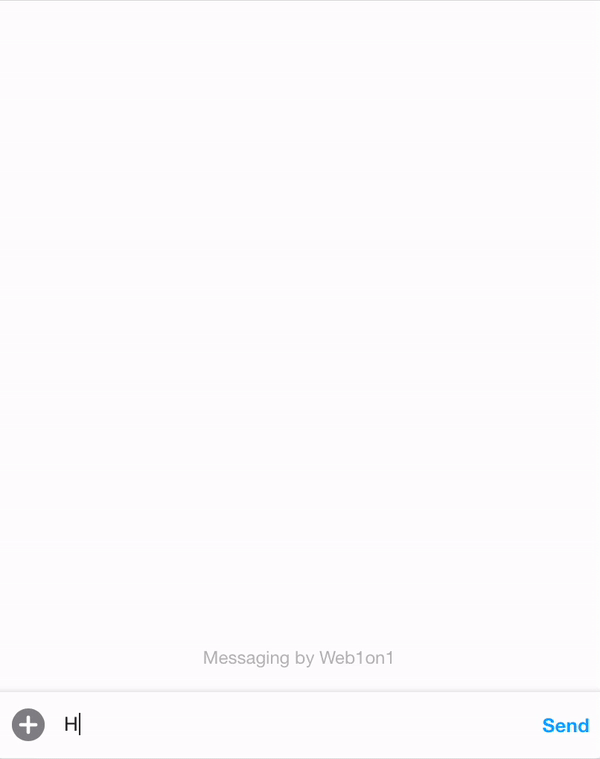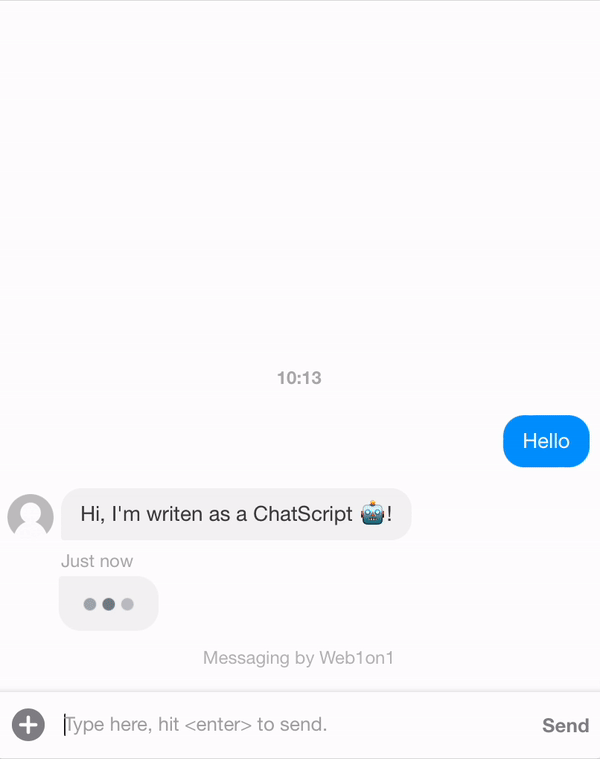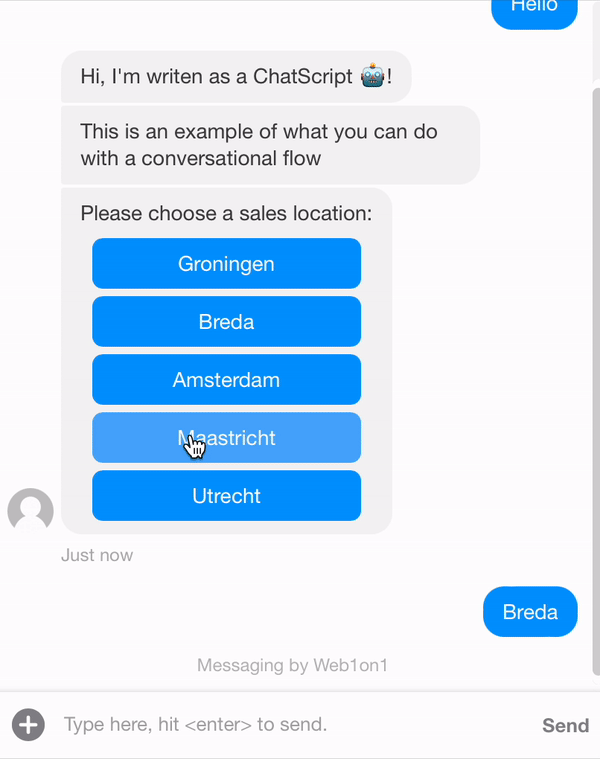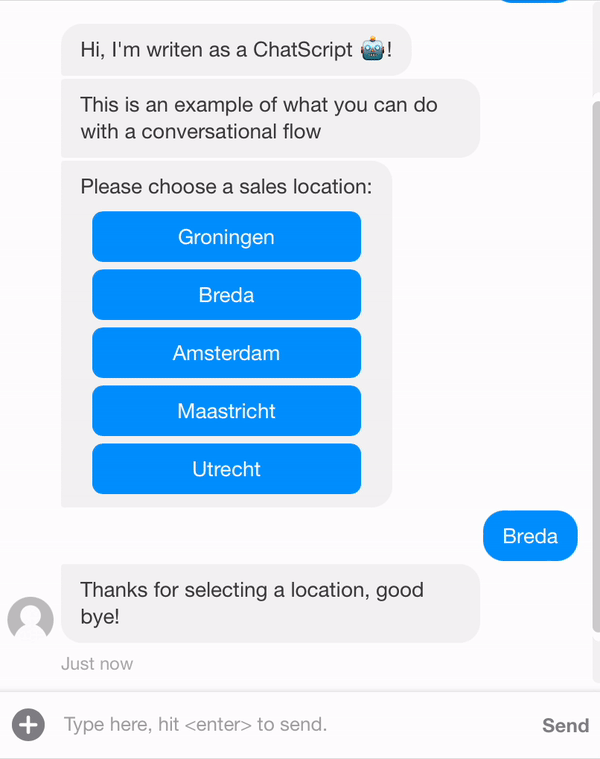
{ "_id": "634408fd849722965483e3c9", "organization": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "orgPath": "631ef94d51892216af7e1054", "type": "template", "name": "Example Conversation", "status": "closed", "messages": [ { "_id": "6344239315dc9888dc428ade", "meta": { "next": "6344127704dffa670c9a0cee", "form": "6344255c52523a19137f37ab" }, "type": "form", "text": "+Example form" }, { "_id": "6344127704dffa670c9a0cee", "meta": { "next": "63441289da876617b2f4a8dc" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Hi, I'm writen as a ChatScript 🤖!" }, { "_id": "63441289da876617b2f4a8dc", "meta": { "next": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a" }, "role": "agent", "text": "This is an example of what you can do with a conversational flow" }, { "_id": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a", "meta": { "next": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc", "modules": [ { "name": "locationSearch.getLocationAndDepartmentSales", "property": "actions" } ] }, "role": "agent", "text": "Please choose a sales location:" }, { "_id": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc", "meta": { "next": "63442b70dae72b60bcdde390" }, "role": "contact", "type": "postback", "text": "postback..." }, { "_id": "63442b70dae72b60bcdde390", "meta": { "next": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Thanks for selecting a location, good bye!" }, { "_id": "6344191651a3e6c81579e9d2", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "agent", "text": "/leave", "type": "command", "delay": 5000 } ] }
When using this flow above, it will show all the sales locations that are currently set in your organisation. So when for example changing the name or adding an extra locations, this will be shown by the ChatScript.
Everytime a module is attached to a message, it needs a name with format: 'modulename'.'methodname' and a property that points a message property (e.g. actions). When a module supports extra options, those can be added via an options attribute.
Supports
- Show all sales locations: locationSearch.getLocationAndDepartmentSales
- Show all service locations: locationSearch.getLocationAndDepartmentService
-
Multiselection: multiselect.default & multiselect.whatsapp
- Needs extra options: title and fields array of strings to show within the conversation.
Multiselect example
{ "_id": "6344128e97e788d83ed9d55a", "meta": { "next": "63441292aed37c83748d0dcc", "modules": [
{
"name": "multiselect.default",
"property": "actions",
"options": {
"fields": [
"Fanta",
"Pepsi",
"Coca-Cola"
],
"title": "Favourite drink"
}
}
] }, "role": "agent", "text": "Please choose your favourite drink" },This message can be added to any flow, keep in mind to change the _id and next.
Exception Handling
A bot flow can sometimes fail as a result of an exceptional circumstance or an "error" that occurred.
Different types of exceptions are possible; we will discuss the two most common.
- Validation errors - at the moment, typically invalid telephone or email entries (we don't validate other fields at the server at the moment)
- Timeout errors - for example, an interaction did not complete within the required time.
To ensure consistency of the bot choreography, several exception handling strategies are conceivable:
- Ignore Error: This unlikely strategy can often be the most effective: do nothing in case of errors
- Isolate Error: ignore the error in the context of the current conversation, but handle all errors afterwards.
- Retry: if you don't succeed at first, try again
- Compensating Action: use a second action that undoes a prior action to regain a consistent state
- Start over: if you cannot undo an action, revert to the beginning and rebuild the desired state.
- Tentative Operation: an interaction is split into two parts, a pending operation, followed by a confirmation or a time-out, which leads to cancellation. (try-confirm-cancel)
- Coordinated Agreement: a dedicated coordinator interacts with participants to find a jointly agreeable solution.
Meta Variables
- failMessage
- failTimes
- timeout
- timeoutMessage
- escalateMessage
Exception Handling Patterns
Consider the following form field capture:
{ "_id": "100", "meta": { "next": "101" }, "role": "agent", "text": "What is your phone number?" },
{ "_id": "101", "meta": { "next": "102" }, "role": "contact", "text": "+31204428899" },
{ "_id": "102", "meta": { "next": "103" }, "type": "field", "text": ".telephone" },
{ "_id": "103", "meta": { "next": "104" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Thanks" },Validation - Ignore error
Not specifying any failMessage meta var will ignore any validation errors, like an invalid phone number
{ "_id": "102", "meta": { "next": "103" }, "type": "field", "text": ".telephone" },Validation - Isolate Error
Specify a meta.failMessage to tell about the error, and move on to the next.
{ "_id": "102", "meta": { "next": "103", "failMessage": "105" }, "type": "field", "text": ".telephone" },
{ "_id": "105", "meta": { "next": "103", "role": "agent", "text": "Invalid phone. No problem, we will email you." },Validation - Infinite Retry
To circle back to the initial question, point meta.next of the failMessage up to the initial question.
{ "_id": "102", "meta": { "next": "103", "failMessage": "105" }, "type": "field", "text": ".telephone" },
{ "_id": "105", "meta": { "next": "100", "role": "agent", "text": "Invalid phone." },Validation - Escalation
Escalate to human agent on first validation error
{ "_id": "102", "meta": { "next": "103", "failMessage": "105" }, "type": "field", "text": ".telephone" },
{ "_id": "105", "meta": { "next": "106" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Sorry, I did not quite get that... No problem, I'll put you through to an agent 🆘" },
{ "_id": "106", "meta": { "next": "107" }, "role": "agent", "type": "command", "text": "/notify" },
{ "_id": "107", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "agent", "type": "command", "text": "/leave", delay: 5000 }Validation - Retry and Escalate
Use failTimes and escalateMessage to break a failMessage cycle (after 2 tries) and further the conversation.
{ "_id": "102", "meta": { "next": "103", "failMessage": "105", failTimes: 2, "escalateMessage": 106", }, "type": "field", "text": ".telephone" },
{ "_id": "103", "meta": { "next": "104" }, "role": "agent", "text": "Thanks" },
{ "_id": "105", "meta": { "next": "100", "role": "agent", "text": "Invalid Phone" },
{ "_id": "106", "meta": { "next": "107" }, "role": "agent", "text": "We'll ask a human to help.." },
{ "_id": "107", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "agent", "type": "command", "text": "/notify" }Timeout - Tentative Operation
Unresponsive contacts can trigger a timeoutMessage on a timeout, to close the conversation.
{ "_id": "100", "meta": { "next": "101"}, "role": "agent", "text": "What is your phone number?" },
{ "_id": "101", "meta": { "next": "102", "timeout": 600, "timeoutMessage": "106" }, "role": "contact", "text": "+31204428899" },
{ "_id": "106", "meta": { "next": "107" }, "role": "agent", "text": "It seems like you're not responding anymore. I'll close the chat now. Feel free to start another one!" },
{ "_id": "107", "meta": { "next": null }, "role": "agent", "type": "command", "text": "/leave", delay: 5000 }A contact response will reset the timer.
Conversation-wide timeout
To set a conversation-wide timeout on contact responses, set the conversations's meta timeout on creation.
POST /v2/conversations
{
type: "script",
messages: [],
meta: {
timeout: 600
timeoutMessage: "106"
}
}or
PATCH /v2/conversations/:id { meta }Using a conversation-wide timeoutMessage, it can be left out of the conversation messages:
{ "_id": "101", "meta": { "next": "102" }, "role": "contact", "text": "+31204428899" },
{ "_id": "106", "meta": { "next": "107" }, "role": "agent", "text": "It seems like you're not responding anymore. I'll close the chat now. Feel free to start another one!" },The conversation.meta timeout will trigger if the contact doesn't respond in 10 minutes. A contact response will reset, a bot response a restart of the timer.